- Afrikan
- Albaniż
- Għarbi
- Belarussu
- Bengali
- Ċek
- Daniż
- Olandiż
- Ingliż
- Finlandiż
- Franċiż
- Galizjan
- Ġermaniż
- Grieg
- Ebrajk
- Ungeriż
- Indoneżjan
- Irlandiż
- Taljan
- Ġappuniż
- Ġavaniż
- każak
- Khmer
- Rwandan
- Korean
- Kirgiż
- Laburista
- Latin
- Latvjan
- Litwan
- Malajan
- Malti
- Mongoljan
- Il-Mjanmar
- Norveġiż
- Persjan
- Pollakk
- Portugiż
- Rumen
- Russu
- Serb
- Slovakk
- Spanjol
- Svediż
- Tagalog
- Tajlandiż
- Tork
- Ukrain
- Vjetnamiż
- Welsh
From ancient pyramids to modern skyscrapers, limestone has served as a foundational material throughout human history. This sedimentary rock forms through the accumulation of marine organisms and minerals over millions of years, creating diverse different types of limestone with unique properties. Some varieties even preserve ancient life forms as fossilized limestone, offering geologists valuable insights into Earth's history. Modern limestone manufacturer operations have refined extraction and processing techniques to meet contemporary construction demands while maintaining sustainable ctices.
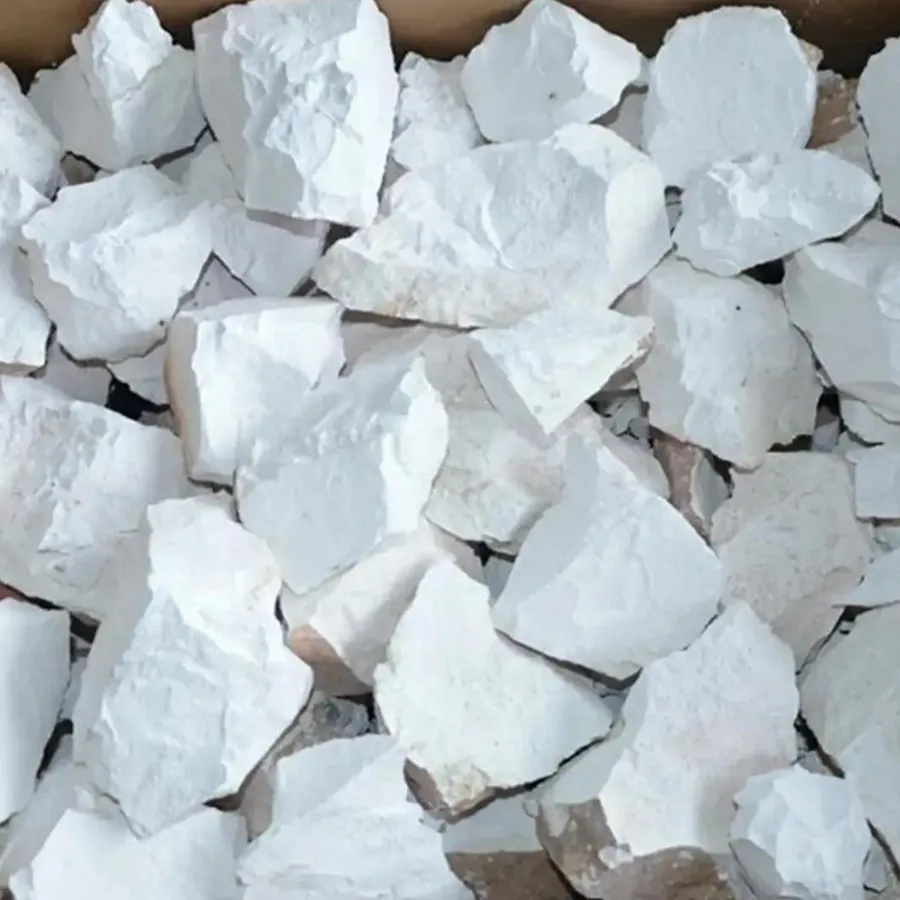

The Geological Origins and Composition of Limestone
Ġebla tal-ġir primarily consists of calcium carbonate deposited from the remains of marine organisms like coral and shellfish. Over geological timescales, these biological materials compress under layers of sediment, gradually forming solid rock. The presence of impurities during formation creates the different types of limestone, ranging from nearly pure calcite varieties to those containing significant clay, sand, or organic matter.
Some limestone formations develop through chemical precipitation in cave systems, creating spectacular stalactites and flowstones. Others form in shallow marine environments where wave action produces oolitic varieties composed of spherical grains. The most visually striking examples often contain well-preserved fossils, earning classification as fossilized limestone. These specimens may showcase ancient shells, coral patterns, or even prehistoric sea creature imprints within their matrix.
Industrial Production Methods of a Modern Limestone Manufacturer
Contemporary limestone manufacturer operations employ sophisticated techniques to extract and process this valuable material while minimizing environmental impact. Quarrying begins with careful geological surveys to identify optimal deposits, followed by precision cutting using diamond-tipped wire saws that reduce waste. Many operations now utilize dust suppression systems and water recycling to maintain ecological balance near extraction sites.
After extraction, raw limestone undergoes crushing and screening to produce various aggregate sizes. For construction-grade material, kilns heat crushed stone to produce quicklime, an essential component in steel manufacturing and water treatment. More refined processing creates powdered calcium carbonate for industrial applications ranging from paper production to pharmaceuticals. Advanced quality control measures ensure each batch meets strict chemical composition standards.
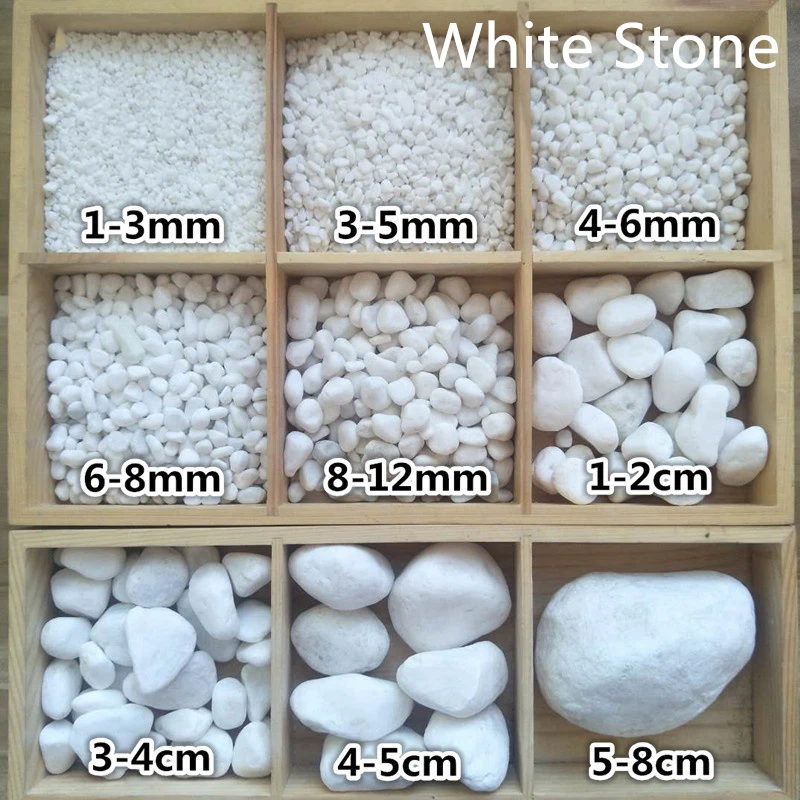
Examining the Different Types of Limestone and Their Applications
The different types of limestone each possess distinct characteristics that determine their ideal uses. High-calcium varieties containing over 95% calcium carbonate serve as premium raw material for cement production and chemical processes. Dolomitic limestone, rich in magnesium carbonate, offers superior durability for construction projects in harsh climates.
Architectural applications frequently specify travertine, a porous limestone formed at mineral springs that develops unique patterning. Fossilized limestone finds special use in decorative applications where its preserved ancient organisms create striking visual interest. Crystalline varieties like Tennessee marble (actually a dense limestone) take exceptional polish for high-end interior finishes.
In agriculture, crushed limestone amendments neutralize acidic soils while providing essential calcium nutrients. Industrial applications consume massive quantities as flux in steel production, filler in manufactured goods, and scrubbing agent in pollution control systems. The material's versatility stems from its wide availability, workability, and chemical properties that remain unmatched by synthetic alternatives.
The Unique Characteristics and Uses of Fossilized Limestone
Fossilized limestone provides a fascinating window into prehistoric ecosystems while serving practical purposes in modern design. These special formations contain clearly visible remnants of ancient marine life, often displaying intricate shell patterns, coral colonies, or even rare fish and plant impressions. The fossilization process occurs when mineral-rich water permeates the remains, gradually replacing organic material with stone while preserving original structures.
Builders and designers value fossilized limestone for its unique aesthetic qualities that blend natural history with visual appeal. When polished, the contrast between the stone matrix and fossil inclusions creates dynamic surfaces unmatched by manufactured materials. Museums and educational institutions frequently incorporate these stones into displays and architecture to emphasize connections between geology and paleontology.
Beyond decorative uses, fossilized limestone shares the functional properties of other limestone varieties. Its durability and workability make it suitable for flooring, wall cladding, and exterior applications where both performance and distinctive appearance matter. Paleontologists continue studying these formations to understand ancient climate conditions and evolutionary biology, making each piece both a construction material and scientific artifact.

Frequently Asked Questions About Limestone
What determines the quality of limestone for construction?
The quality of limestone depends on its chemical purity, compressive strength, and porosity. Construction-grade material typically has low water absorption and high density to withstand structural loads and weathering.
How can you identify genuine fossilized limestone?
Authentic fossilized limestone will show clear biological structures with three-dimensional detail under magnification. The fossils should integrate seamlessly with the stone matrix rather than appearing as surface decorations.
What environmental considerations do limestone manufacturer operations face?
Responsible limestone manufacturer practices address dust control, water management, and habitat protection. Many operations implement land reclamation programs to restore quarried areas to natural ecosystems.
Why are there so many different types of limestone?
The different types of limestone result from variations in original sediment composition, formation pressure, mineral content, and fossil inclusions. These factors create stones with distinct appearances and performance characteristics.
Can limestone be used in modern sustainable architecture?
Ġebla tal-ġir remains relevant in green building for its natural thermal mass, durability, and low processing energy compared to synthetic materials. Properly sourced, it contributes to sustainable design strategies.
The enduring importance of limestone across industries and eras testifies to its unmatched combination of practicality and beauty. From its geological origins to contemporary applications, this remarkable material continues to shape our built environment while preserving Earth's ancient history in its very structure. As extraction and fabrication technologies advance, limestone maintains its position as both a link to our past and foundation for future development.
Aħbarijiet Relatati