- africano
- albanés
- árabe
- bielorruso
- bengalí
- checo
- danés
- Holandés
- Inglés
- finlandés
- Francés
- gallego
- Alemán
- Griego
- hebreo
- húngaro
- indonesio
- irlandés
- italiano
- japonés
- javanés
- kazajo
- Jemer
- Ruandés
- coreano
- Kirguistán
- Mano de obra
- latín
- letón
- lituano
- malayo
- maltés
- mongol
- Myanmar
- noruego
- persa
- Polaco
- portugués
- rumano
- ruso
- serbio
- eslovaco
- Español
- sueco
- Tagalo
- tailandés
- turco
- ucranio
- vietnamita
- galés
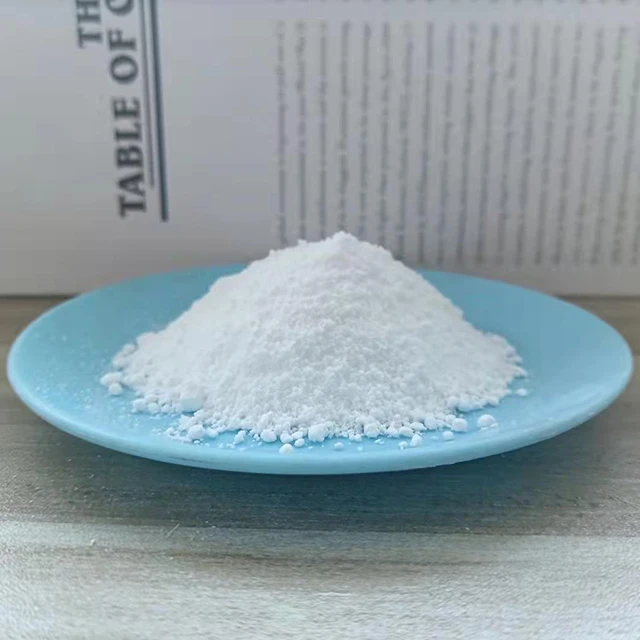
The chemical formula of potassium feldspar is a key piece of information for those working with or studying this essential mineral. Potassium feldspar, also known as K-feldspar, is one of the most abundant minerals in the Earth's crust and plays a significant role in the formation of granite and other igneous rocks. Its chemical formula of potassium feldspar is typically represented as KAlSi₃O₈, indicating that it consists of potassium (K), aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), and oxygen (O) atoms.
This mineral is widely used in ceramics, glass-making, and as a flux in the production of bricks and tiles due to its high content of potassium. The chemical formula of potassium feldspar makes it an important source of potassium in agriculture, contributing to soil fertility when processed and used as a soil amendment. Its presence in rocks and soils can significantly affect the chemical composition of the environment, making it an essential mineral for both geological studies and industrial applications.

Potash Feldspar Chemical Formula
When discussing potassium feldspar, it is common to come across the term potash feldspar chemical formula. This refers to a specific group of feldspar minerals that contain potassium as their primary alkali metal component. The potash feldspar chemical formula is also represented by KAlSi₃O₈, which is the same as potassium feldspar. However, "potash" is often used to differentiate this specific feldspar mineral due to its high potassium content, which makes it an excellent source of potassium for various industrial and agricultural uses.
The potash feldspar chemical formula is important in the ceramics and glass industries, where the potassium within the feldspar helps lower the melting temperature of silica and promotes the production of durable and high-quality products. In agriculture, the high potassium content makes it a useful mineral for soil enrichment and plant growth. The potash feldspar chemical formula also underscores its potential in a wide range of applications, including in the manufacturing of glazes, tiles, and certain chemicals.
Potassium Feldspar Thin Section
A potassium feldspar thin section is an essential tool used by geologists and mineralogists to study the properties and structure of this mineral in detail. When a sample of potassium feldspar is cut into a thin slice and mounted on a microscope slide, it is called a potassium feldspar thin section. This thin section allows for the mineral to be examined under a polarized light microscope, providing valuable insights into its crystallography, mineral composition, and optical properties.
The study of a potassium feldspar thin section can reveal important details about the mineral's internal structure, such as its crystal habit, twinning, and the presence of inclusions. These characteristics are crucial for understanding the conditions under which the feldspar formed and can help in identifying it in various rock types. The potassium feldspar thin section is a key tool in geological research and can also be used in mineral identification for both academic and industrial purposes.
Potassium Feldspar Characteristics
Understanding the potassium feldspar characteristics is essential for recognizing this mineral in different geological environments and for its practical uses. Potassium feldspar characteristics include its crystal structure, hardness, color, and cleavage properties. It typically forms in monoclinic or triclinic crystal systems and can appear in a range of colors from white, cream, pink, and red, to brown, depending on the trace elements present.
One of the most notable potassium feldspar characteristics is its hardness on the Mohs scale, which ranges from 6 to 6.5, making it relatively hard and durable. This property makes potassium feldspar a valuable component in the manufacture of glass and ceramics. Additionally, potassium feldspar characteristics such as its high potassium content contribute to its ability to lower the melting point of silica, making it a crucial ingredient in the production of tiles, glazes, and other high-temperature materials. Its ability to weather into clay minerals also contributes to its importance in soil science and agriculture.
Potassium Feldspar Characteristics FAQs
What is the chemical formula of potassium feldspar?
The chemical formula of potassium feldspar is KAlSi₃O₈, which consists of potassium, aluminum, silicon, and oxygen.
How is potash feldspar different from potassium feldspar?
While both share the same potash feldspar chemical formula (KAlSi₃O₈), the term "potash" refers specifically to feldspar with high potassium content, often used in industrial applications like ceramics and glassmaking.
What is the purpose of a potassium feldspar thin section?
A potassium feldspar thin section is used to study the mineral's internal structure and properties under a microscope, providing insights into its crystallography, optical properties, and mineral composition.
What are the key characteristics of potassium feldspar?
The potassium feldspar characteristics include its crystal structure (monoclinic or triclinic), hardness (6-6.5 on the Mohs scale), and range of colors from white to pink, as well as its use in glass and ceramic production.
How does potassium feldspar contribute to agriculture?
The high potassium content in potassium feldspar makes it valuable as a natural soil amendment, helping to improve soil fertility and promote plant growth by providing potassium to plants.
Noticias relacionadas